If your server is running out of disk space, Docker containers are often the silent culprits. Their log files can grow indefinitely if not configured correctly. Here is a quick 3-step guide to finding the largest logs, identifying which container they belong to, and truncating them without restarting your services.
1. Check Docker Log Sizes
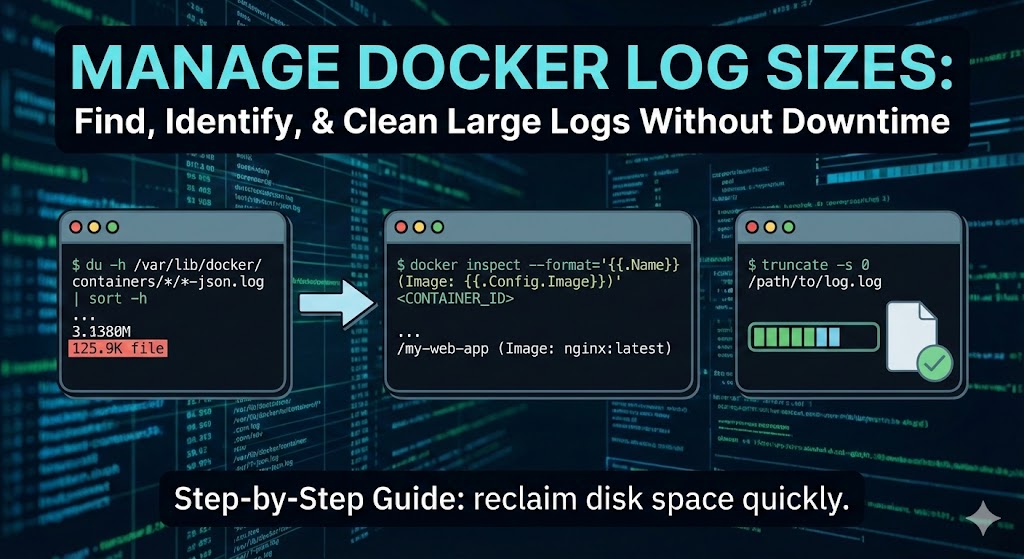
First, let’s find out which containers are consuming the most space. Run the following command to list all Docker JSON log files, sorted by size:
du -h /var/lib/docker/containers/*/*-json.log | sort -hOutput Example:
12M /var/lib/docker/containers/a1b2c3d4e5.../a1b2c3d4e5...-json.log
500M /var/lib/docker/containers/f9e8d7c6b5.../f9e8d7c6b5...-json.log
2.1G /var/lib/docker/containers/3424cd7620.../3424cd7620...-json.logThe last entry in the list is your largest log file.
2. Identify the Container
The output above gives you the Log Path, which includes the full Container ID. For example, in the path /var/lib/docker/containers/3424cd7620..., the string 3424cd7620... is the Container ID.
To find the human-readable Name and Image associated with that ID, use the docker inspect command:
docker inspect --format='{{.Name}} (Image: {{.Config.Image}})' <CONTAINER_ID>Example:
docker inspect --format='{{.Name}} (Image: {{.Config.Image}})' 3424cd7620Output:
/my-web-app (Image: nginx:latest)Now you know exactly which application is spamming your disk!
3. Truncate the Log File
Deleting the log file directly (using rm) is dangerous because Docker may not release the file handle, meaning the disk space won’t be freed until you restart the container.
Instead, use the truncate command to clear the file content while keeping the file itself intact. This frees up space immediately without downtime.
Command:
truncate -s 0 /var/lib/docker/containers/<CONTAINER_ID>/<CONTAINER_ID>-json.logPro Tip: If you want to truncate the specific file you found in Step 1, you can copy and paste the full path directly:
truncate -s 0 /var/lib/docker/containers/3424cd7620.../3424cd7620...-json.logYour disk space is now reclaimed!

![Read more about the article [Android] Show WebView as Dialog using Jetpack Compose](https://devslinger.fyi/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/unnamed-2-300x164.jpg)
![Read more about the article [Linux] Create App Shortcut for Application in Linux](https://devslinger.fyi/wp-content/uploads/2025/11/create_app_shortcut_linux-300x125.jpg)
